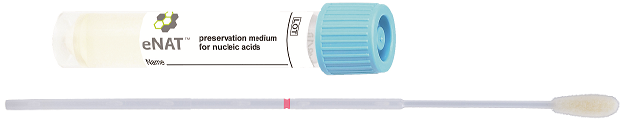
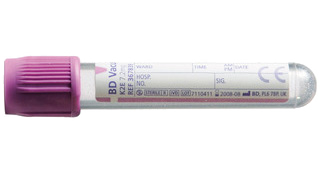
Immunodeficiency (MAC)
Bestel het onderzoek
57,48
47,50 (excl. 21% BTW)
Omschrijving
Doeldiersoort en rassen
Hond
Middenslagschnauzer
Staalname
- Wisser genetisch
- EDTA volbloed
Doorlooptijd
14 dagen
